Nepal Rastra Bank i.e. Nepal’s Central Bank has released the recent macroeconomic and financial situation report based on the annual data of 2022/23 i.e. FY 2079/80 in Nepali date.
Inflation
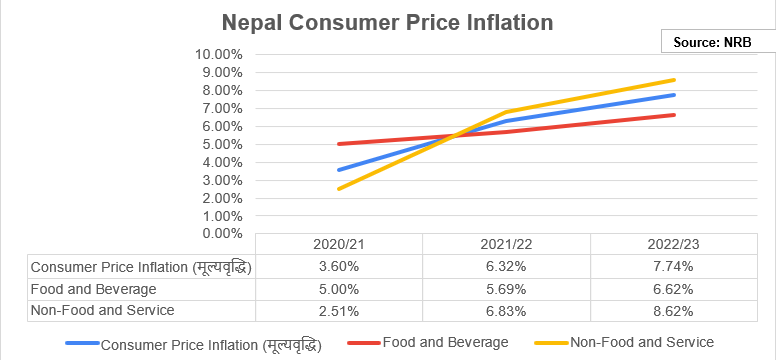
The Bank reported the annual average consumer price inflation at 7.74% compared with a CPI of 6.32% last year. The Central Bank targeted to keep the CPI within 7% range during that period. The Food and Beverage component rose by 6.62% while the Non-Food and Services prices rose by 8.62% during the current period.
India’s retail inflation stood at 7.44% y-o-y in July which is above the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) tolerance band of 2-6%. Since Nepal has adopted a fixed currency peg with India and both countries share open borders so the price developments in Nepal are largely determined by the broader price levels in India. The estimates from the IMF Working Paper indicate that the passthrough time of inflation from India to Nepal is about seven months (IMF Report).
GDP Growth and Composition
The GDP growth rate of Nepal for the year 2022/23 remained at 1.86% according to the National Statistics Office. The GDP growth was 5.62% last year and 4.84% two years ago. The sector which grew the largest was the agriculture sector followed by Service sector and Industry sector.
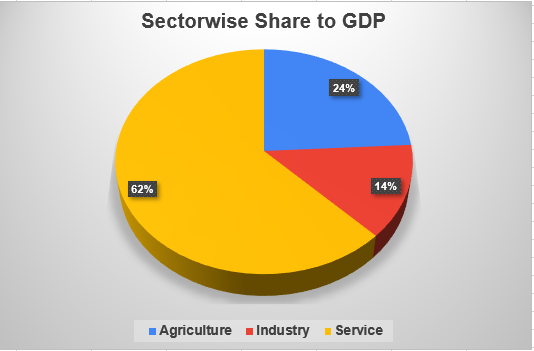
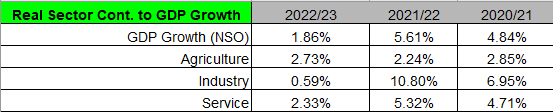 The Nepalese Economy is heavily dependent on the service sector which shares around 62% of GDP. The Agriculture and Industry sector share 24% and 14% of GDP respectively.
The Nepalese Economy is heavily dependent on the service sector which shares around 62% of GDP. The Agriculture and Industry sector share 24% and 14% of GDP respectively.
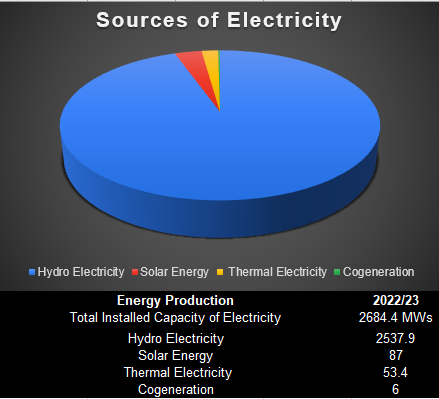
The Tourism sector has bounced back after the COVID-19 restrictions. The number of new tourist arrivals increased from 374,147 in 2021/22 to 862,992 in 2022/23 which is a 130% rise. The installed capacity of Electricity stood at 2684.4 megawatts.
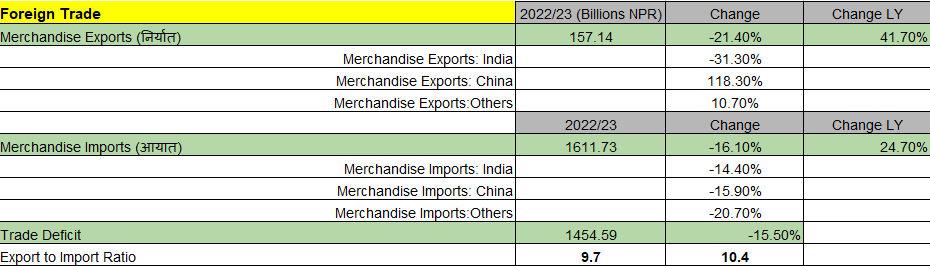
Foreign Trade
The Merchandise Exports fell by 21.40% and remained at Rs. 157.14 Billions. The Merchandise Imports fell by 16.10% this year and remained at Rs. 1611.73 Billions due to the contractionary monetary policy implemented by the Central Bank. This was done to prevent further erosion of the foreign exchange reserves which severely decreased after the sharp economic recover after the COVID-19 pandemic. Hence, the Trade deficit also fell by 15.5% to Rs. 1454.59. The Export to Import Ratio for this year was 9.7 which was 10.4 in the previous year.
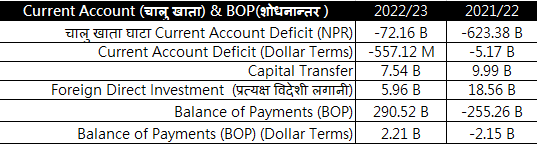
Balance of Payments and Remittances
The Current Account Deficit has improved in this year but is still at Rs. 72.16 Billions. The Current Account Deficit was Rs. 623.38 Billion last year. In Dollar terms, The Current Account deficit fell to $557.12m from $5.17b.
The Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) declined to Rs. 5.96B from Rs. 18.56B. The most improved figure is the Balance of Payments which remained in the positive territory. The BOP which was Rs. -255.36b last year stood at Rs. 290.52b this year. In Dollar terms, the Balance of Payments rose to $2.21B from $-2.21B.
The Net Services Income remained at the deficit of Rs. 83.83b. International Payments for Education this year rose significantly to Rs. 100b from Rs. 67.7b last year.
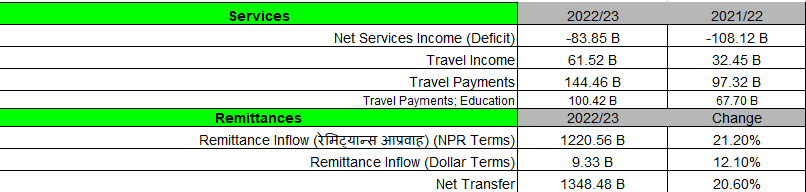
The remittance inflow increased by 21.2% in NPR terms and 12.10% in Dollar terms. The Nepalese currency vis-à-vis US dollar depreciated 2.79% in the year 2022/23.
Source: Nepal Rastra Bank
https://www.nrb.org.np/
https://www.nrb.org.np/contents/uploads/2023/08/Current-Macroeconomic-and-Financial-Situation-English-Based-on-Annual-data-of-2022.23.pdf





